This article was last updated on January 25, 2024 to expand code examples add more real use-cases for React useCallback hook.
Introduction
This post is about using the React useCallback() hook. We demonstrate the use of useCallback in a React component and examine how it impacts performance in a demo app.
This is the third and final part of the React Memoization Series hosted on Refine.dev blog.
The preceding two parts are:
In this post, we explore how to use React useCallback in order to memoize a function passed from a parent to a child component. We follow up by making changes to the demo blog app in Part II and try to understand how function memoization using useCallback gives performance gains to a React app.
Steps we'll cover:
- What is React
useCallback? - Memoize Functions with React
useCallback: Ensuring A Callback's Referential Equality - When to Use React
useCallback - When Not to Use React's
useCallbackHook
What is React useCallback ?
React useCallback() is a hook that memoizes a function definition and ensures its referential integrity between re-renders of a React component. It works by accepting the function as an argument, memoizing it, and then returning the memoized function. The memoized function then can be passed down to child components and invoked from therein.
Memoization of a function definition with useCallback helps optimize a React component by preventing unnecessary re-renderings originating from a change in the function's object identity.
Why Use React useCallback Hook?
In React, callback functions like event handlers inside a component create new individual function objects at every re-render of the component. This behavior breaks referential equality of callbacks passed to and invoked inside a child component.
For example, in a case where a callback is passed from a parent component to a child as a prop, by default, the child receives a new copy of the callback at every render of the parent. This leads to an additional re-render in the child component just because of the change in the accepted function object's identity. Such unnecessary re-renders add to the app's cost. So, callback functions in React should be memoized in a way that they maintain referential integrity across re-renders of a parent component.
Memoizing a callback in React with useCallback() helps ensure the function's referential integrity and prevent these re-renders. useCallback() works by storing the function object itself. So, every time the parent re-renders, the same callback object is passed to the child and the child's re-render is prevented.
Memoize Functions with React useCallback: Ensuring A Callback's Referential Equality
In the sections ahead, inside the demo blog app, we first examine the way a callback, deletePost, passed to a child component (<UserPostsList />) by default triggers unnecessary re-renders. We then implement memoization of the callback function with the useCallback hook and observe how it prevents these re-renders.
Prior to that, let's first get familiar with the code we are dealing with.
Project Content Overview
The demo app is the same one we have been using in the React Memoization Series. It is based on the idea of a list of posts on a blog.
We recommend you follow along from Part I and II. This way, you should already have the app cloned, opened in a code editor, installed, and up and running in a browser.
There are several components involving a user seeing the latest posts and a list of the user's posts. Allow yourself some time to understand the components individually, their relationships and their state changes. You should especially be familiar with what's going on in the <UserPostsIndex />, <UserPostsList /> and <UserPosts /> components before we make the changes to with useCallback.
The discussion of this article is focused on optimizing performance by memoizing callback functions that are passed as a prop from a parent component to a child. We are going to use the useCallback() hook for this.
Code Investigation
As we're already familiar with the <App /> and <Blog /> components from Part I and II, in this post, we'll start with the<UserPostsIndex /> component. It looks like this:
import React, { useEffect, useState } from "react";
import fetchUserPosts from "../fetch/fetchUserPosts";
import UserPostsList from "./UserPostsList";
const UserPostsIndex = ({ signedIn }) => {
const [userPosts, setUserPosts] = useState([]);
const deletePost = (e) => {
const { postId } = e.currentTarget.dataset;
const remainingPosts = userPosts.filter((post) => post.id !== parseInt(postId));
setUserPosts(remainingPosts);
};
useEffect(() => {
const posts = fetchUserPosts();
setUserPosts(posts);
}, []);
return (
<div className="my-1 p-2 box">
<div className="m-1 py-1">
<h2 className="heading-md">Your Posts</h2>
<p className="m-1 p-1">{signedIn ? `Signed in` : `Signed out `}</p>
{userPosts && <div className="px-1">{<UserPostsList userPosts={userPosts} deletePost={deletePost} />}</div>}
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default React.memo(UserPostsIndex);
As you can see, <UserPostsIndex /> receives signedIn as a prop from <Blog />. It then fetches the user's posts and sets userPosts when the component mounts.
In the JSX, a <UserPostsList /> component is rendered with deletePost function passed to it, along with userPosts.
The <UserPostsList> component looks like this:
import React from "react";
import UserPost from "./UserPost";
const UserPostsList = ({ userPosts, deletePost }) => {
console.log("Rendering UserPostsList component");
return (
<div className="px-1">
{userPosts.map((post) => (
<div key={post.id} className="my-1 box flex-row">
<UserPost post={post} />
<button className="btn btn-danger" data-post-id={post.id} onClick={deletePost}>
Delete
</button>
</div>
))}
</div>
);
};
export default React.memo(UserPostsList);
Here, we are receiving the userPosts array and the deletePost callback. In the JSX, we map a <UserPost /> to each post in userPosts array and invoke deletePost() to remove a post from the list.
<UserPost /> is a presentational component where we display the title as a link. It looks like this:
import React from "react";
const UserPost = ({ post }) => {
// console.log('Rendering UserPost component')
return (
<div className="my-1 flex-row-left">
<a href={`#${post.title}`} className="">
<h4 id={post.title} className="px-2 font-sm font-bold">
{post.title}
</h4>
</a>
</div>
);
};
export default UserPost;
Referential Inequality of Callbacks: Observing Unnecessary Re-renders
As you can already tell, deletePost is a callback function expected cause re-renders of <UserPostsList />. In order to observe them, let's add the following to <UserPostsIndex />:
console.log("Rendering UserPostsIndex component");
And this one to <UserPostsList />:
console.log("Rendering UserPostsList component");
If we check our console now, we can see the logs showing the initial rendering of these components.
Then if we click the SignOut button on the navbar, we see batches of renders originating from <UserPostsIndex />, <UserPostsList /> and <UserPost />:
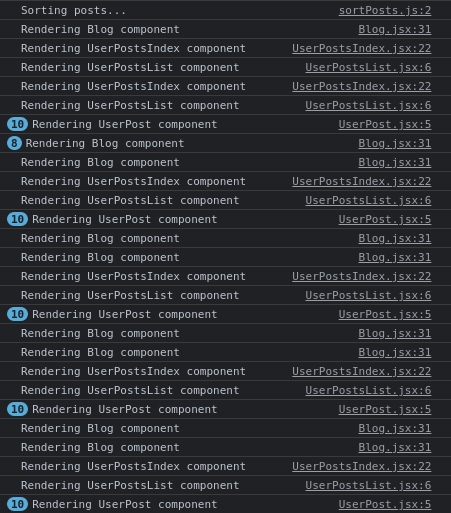
It is possible to account for the re-render of <UserPostsIndex /> because the value of the signedIn prop changed when we clicked Sign Out.
However, re-rendering of <UserPostsList /> at first does not make sense because we expect it to re-render when only userPosts change. And userPosts does not change with the change in the value of signedIn. And since nothing else is notably changing.
Also, we already memoized <UserPostsList /> with React.memo() to prevent its re-renders due to changes in any of its ancestors' state.
But curious, if deletePost changes ?
Well, it does. It changes due to referential inequality because at every re-render of <UserPostsIndex />, a new deletePost function object is spun into runtime. This change in object identity triggers a re-render in <UserPostsList />. The way it is happening above is, when we change signedIn, <UserPostsIndex /> re-renders, creates and passes in a new version of deletePost and causes <UserPostsList /> to re-render.
Memoizing an Event Listener with useCallback()
Now, memoizing deletePost would deliver the same function object at every re-render of <UserPostsIndex />. So, let's memoize it with useCallback() by making the following changes in <UserPostsIndex />:
import React, { useCallback, useEffect, useState } from "react";
const UserPostsIndex = ({ signedIn }) => {
const deletePost = useCallback(e => {
const { postId } = e.currentTarget.dataset;
const remainingPosts = userPosts.filter(post => post.id !== parseInt(postId));
setUserPosts(remainingPosts);
}, [userPosts]);
...
};
export default React.memo(UserPostsIndex);
Now, if we click the Sign Out button a few times, we'll see in the console that <UserPostsIndex /> is re-rendered, but <UserPostsList /> and <UserPost /> are not:

This is because useCallback() caches and produces the same copy of deletePost at every render of <UserPostsIndex />. So referential integrity of deletePost is maintained and it prevents unnecessary re-renderings of <UserPostsList />, contributing to performance optimization of the component.
React useCallback with Dependencies
Notice we are passing a dependency in the array passed as the second argument of useCallback. With userPosts as a dependency, we want a change in userPosts to trigger a renewal of the function memo. So, every time the value of userPosts changes, a new deletePost function object will be created in <UserPostsIndex /> and <UserPostsList /> will be re-rendered.
When to Use React useCallback
React useCallback hook is intended to memoize a callback function by maintaining its referential integrity. It should not be confused with useMemo which is used to cache the value of a function.useCallback is commonly used for memoizing functions between re-renders.
Other Cases
React useCallback() is also used to cache callbacks in debouncing, as well as preventing firing of events typically in useEffect() hooks.
When Not to Use React's useCallback Hook
We should not use the useCallback hook for memoizing the value of a function. We should also avoid overusing useCallback since the hook itself contributes to the component's cost. It is recommended to use the useCallback hook only in cases referential equality of the function is important.
Summary
In this post, we demonstrated how to leverage the React useCallback hook in preventing unnecessary re-renderings originating from a callback function's referential inequality.
We first observed from the browser's console how a callback passed to a child component triggers useless re-renders due to change in the function's object identity. We then learned how to prevent them by implementing the callback's memoization with React's useCallback() hook which helps us produce the same function object at every re-render of the parent.
Example
npm create refine-app@latest -- --example blog-react-memoization-memo